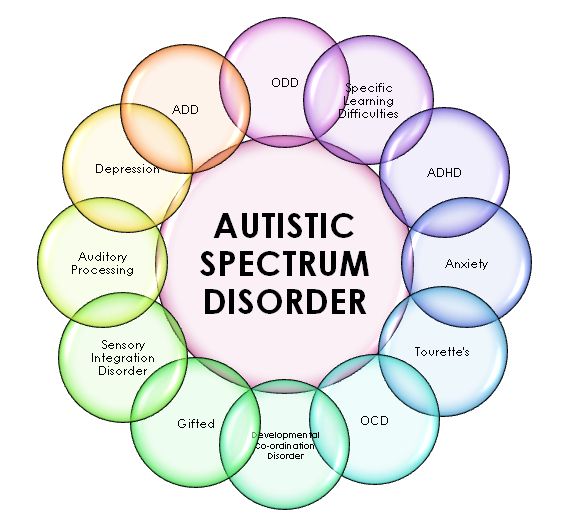
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) presents unique challenges in communication, necessitating a nuanced understanding of how these individuals express themselves and engage with others. Recognizing that communication forms the bedrock of human interaction, embracing effective strategies tailored to individuals on the spectrum becomes paramount. This exploration delves into various communication strategies, offering insights into how to foster meaningful connections.
1. Visual Supports
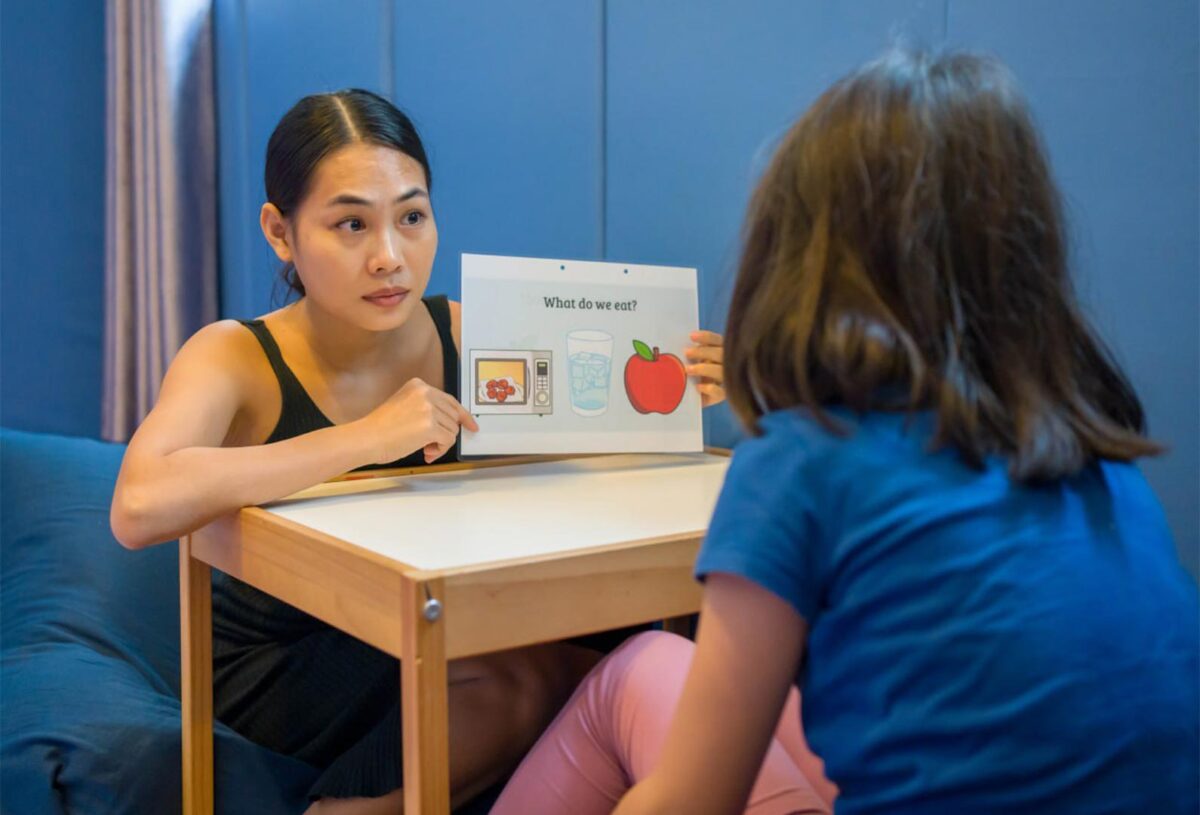
One of the most effective strategies for enhancing communication for individuals with autism is the integration of visual supports. These tools—ranging from pictorial schedules to social stories—aid comprehension and expression by providing clear, concrete representations of abstract concepts. Visual aids cater to the preference for visual learning that many individuals on the spectrum exhibit, facilitating a smoother exchange of information. For example, employing a simple image of a sun to signify “playtime” or a picture of a snack can help bridge the gap between intent and understanding. This method not only eases anxiety surrounding unpredictable changes but also empowers individuals, allowing them to express their needs and desires more readily.
2. Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC)
For some, verbal communication may be a daunting or unattainable task. In such cases, Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) systems become invaluable. These range from low-tech options like communication boards and symbol cards to high-tech solutions involving speech-generating devices. By leveraging AAC, individuals can convey messages effectively, thus enhancing their ability to participate in social interactions. Familiarization with these tools must be a priority, ensuring that users feel comfortable and confident in expressing themselves. Training caregivers and educators to use AAC methods proficiently is equally crucial, thereby creating a consistent communication environment.
3. Modeling and Naturalistic Teaching
Modeling appropriate language and social interaction through naturalistic teaching strategies is another powerful method. When caregivers, peers, and educators embody desired communicative behaviors within a variety of contexts, they serve as living examples, demonstrating how to engage in conversations or express needs. This approach can be employed during everyday activities—like playtime or while eating—allowing learners to observe and imitate relevant behavior in a real-world environment. Encouragement of peer interactions can further foster imitation and reinforce communication skills, laying the groundwork for social competence.
4. Social Skills Training
Training in social skills is integral to augmenting communication efficacy. Tailored programs can help individuals navigate social nuances, decode nonverbal cues, and respond appropriately in various situations. Role-playing exercises, group activities, and structured social scenarios can provide a safe space for practice. By explicitly teaching aspects such as turn-taking, active listening, and understanding personal space, individuals with autism can attain greater proficiency in social engagement. This step not only enhances their communicative repertoire but also builds their confidence in social settings.
5. Clear and Consistent Language
Clarity and consistency in language are essential when communicating with individuals on the spectrum. Using concise sentences, avoiding idioms, and refraining from abstract language can significantly reduce misunderstanding. The principle of ‘less is more’ often applies; therefore, articulating thoughts straightforwardly while allowing for processing time can make interactions smoother. Additionally, consistency in the language used—such as sticking to specific terms for objects or activities—helps individuals associate words with meaning, thereby reinforcing comprehension.
6. Emotional Communication Tools
Understanding and expressing emotions can pose a significant barrier for individuals with autism. Implementing emotional communication tools, like feelings charts or emoji cards, can facilitate conversations about emotions. Such tools allow individuals to label their feelings and articulate their emotional states. By fostering an awareness of emotions, both their own and those of others, one can significantly enhance social interactions and collaborative engagements. Teaching empathy alongside these tools cultivates deeper connections and understanding.
7. Technology as a Supportive Ally
In our technology-driven world, innovative applications designed to support communication for individuals with autism are burgeoning. Various programs offer features such as speech synthesis, vocabulary building, and interactive story comprehension. These digital aids can serve as both educational tools and sources of engagement, linking individuals to a broader community and enhancing their communicative abilities. Encouraging the use of technology must be complemented with supervision to ensure that it enriches rather than distracts from real-life interactions.
8. Collaboration and Support Networks
Finally, the importance of collaboration and establishing a support network cannot be overstated. Engaging parents, educators, therapists, and peers creates a holistic approach to communication strategies. Regular meetings, workshops, and training programs can ensure everyone involved is equipped with the necessary tools and strategies. Open lines of communication among this network foster consistency, providing a unified approach to communication, which greatly benefits individuals with autism.
In summation, effective communication strategies for individuals with autism are multifaceted and require a thoughtful, tailored approach. By employing visual aids, AAC, modeling, and training while embracing technology and fostering collaboration, we create an inclusive environment fostering self-expression and enabling individuals on the spectrum to navigate the complex world of communication with greater ease. The journey towards effective communication is an evolving process, one that necessitates patience, empathy, and continuous learning.