Living with autism is a multifaceted journey that encompasses a spectrum of experiences, challenges, and triumphs. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition characterized by a range of symptoms and abilities, affecting communication, social interaction, and behavior. This article delves into various aspects of living with autism, offering insights into challenges faced, strategies for support, and how society can foster inclusivity.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
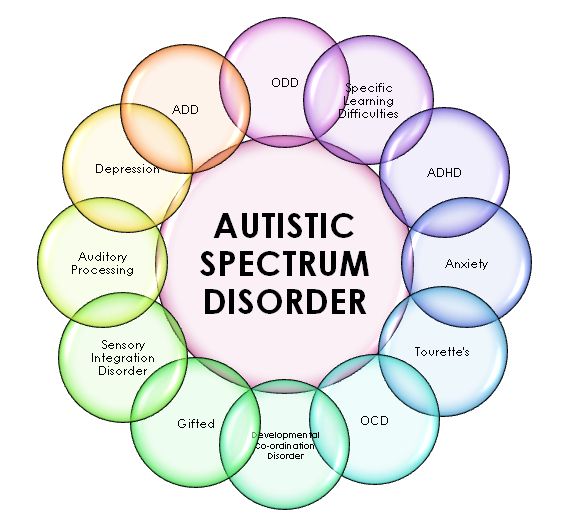
Autism is categorized into different types, with individuals exhibiting a unique combination of behaviors and skills. The spectrum ranges from mild to severe forms, often defined in terms of the intensity of symptoms. Some individuals may have exceptional abilities in specific areas, such as mathematics or music, while others may face significant challenges in daily living tasks. Understanding these variations is the cornerstone of fostering effective communication and accommodation strategies.
Common Challenges Faced
Daily life for individuals with autism can be rife with obstacles. Sensory processing issues are prevalent; many individuals may experience hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to sensory stimuli such as light, sound, and touch. This can lead to overwhelming experiences in environments that most consider routine.
Social communication presents another significant hurdle. Understanding non-verbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions, can be particularly daunting. As a result, individuals may find it challenging to navigate social interactions, leading to potential isolation or misunderstanding in social settings.
Furthermore, meltdowns or shutdowns can occur when faced with overwhelming situations. These reactions may manifest as intense emotional outbursts or withdrawal from the environment, underscoring the importance of recognizing and addressing sensory overload.
Educational Environments
Education plays a pivotal role in the development of individuals with autism. Specialized educational settings can provide tailored support that meets the unique needs of students. Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are critical tools that outline personalized goals, ensuring that students receive appropriate interventions and accommodations.
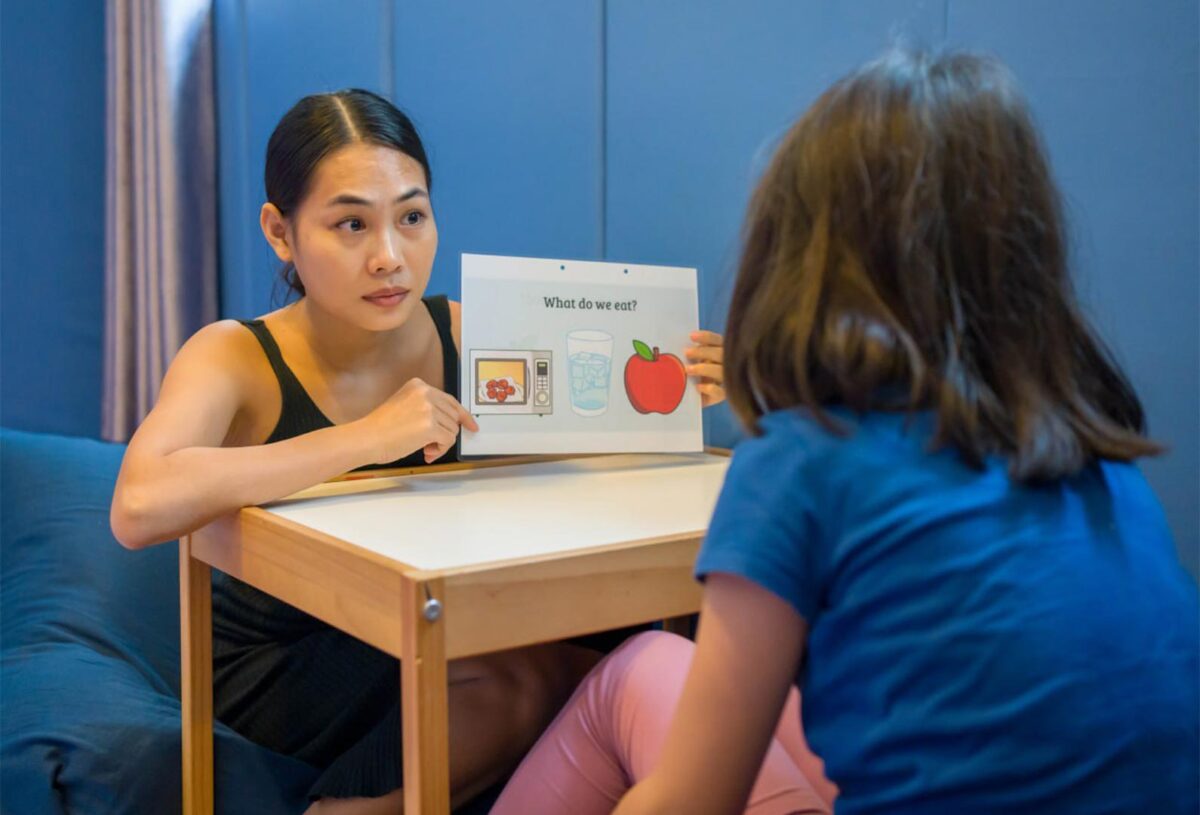
Integrating technology into educational settings can also enhance learning experiences. Tools such as speech-generating devices, visual schedules, and interactive learning apps can facilitate communication and engagement, empowering students to thrive academically.
Moreover, fostering an inclusive classroom environment is essential. Encouraging peer support and understanding can help bridge the gap between neurotypically developing students and those with autism, promoting empathy and collaborative learning experiences.
Social Support and Family Dynamics
Families navigating the complexities of autism often find themselves in need of robust support networks. Parent training and support groups can offer invaluable resources, providing emotional support while sharing practical strategies for managing day-to-day challenges.
Siblings of individuals with autism may also require guidance. Educating siblings about autism can help them develop empathy and understanding toward their brother or sister, fostering stronger familial bonds. Engaging in family activities that account for diverse sensory and social needs can further enrich familial interaction.
As family dynamics evolve, it is essential to recognize and respect the individualism of each family member. Open discussions about each person’s feelings and experiences can enhance understanding and support within the family unit.
Coping Strategies and Therapeutic Approaches
A plethora of coping strategies can assist individuals with autism in managing their daily lives. Mindfulness techniques, such as breathing exercises and grounding exercises, can help reduce anxiety and promote emotional regulation. Engaging in hobbies or interests can also provide a necessary outlet for stress and serve as a means of self-expression.
Therapeutic interventions, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Occupational Therapy (OT), and Social Skills Training, are instrumental in supporting skill development and addressing specific challenges. These therapies can be tailored to fit individual needs, ensuring that individuals acquire practical skills for daily living and social interaction.
Embracing Autonomy and Independence
As individuals with autism transition into adulthood, a focus on independence and self-advocacy becomes paramount. Teaching self-advocacy skills equips individuals with the tools to express their needs and preferences effectively. Understanding one’s rights within educational, workplace, and community environments can foster confidence and empower individuals to pursue their aspirations.
Life skills training, encompassing areas such as budgeting, cooking, and transportation, can facilitate a smoother transition into independent living. Programs that focus on vocational training can prepare individuals for employment, providing them with essential skills needed in the workforce, thereby promoting economic autonomy.
Community Engagement and Advocacy
Community engagement plays a crucial role in reshaping perceptions of autism. Awareness campaigns, workshops, and community events can educate the public on autism, promoting understanding and empathy. Advocacy efforts are essential in pushing for policy changes that enhance accessibility, support, and inclusion for individuals with autism.
Participating in local organizations that focus on autism awareness and acceptance provides individuals and their families with resources while fostering a sense of connection and belonging. Advocacy not only empowers individuals with autism but also enriches the community as a whole.
The Road Ahead
Living with autism presents both challenges and opportunities. By embracing a holistic understanding of autism and advocating for inclusive practices, society can pave the way for individuals with autism to flourish. Fostering understanding, enabling access to resources, and promoting empathy will lead to more supportive environments where individuals can nurture their unique abilities and contributions.
In conclusion, living with autism is not merely a matter of coping with challenges; it is an invitation to a wider spectrum of experiences. As society continues to evolve, the integration and acceptance of individuals on the autism spectrum are vital for cultivating a richer, more diverse community.