Transitioning to adulthood is a pivotal stage in the lives of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This journey encompasses a myriad of challenges, opportunities, and experiences that significantly shape their future. To navigate this complex process effectively, it’s imperative to understand the various components that facilitate a successful transition and empower these individuals to lead fulfilling lives.
1. Understanding the Nature of Autism and Its Unique Challenges
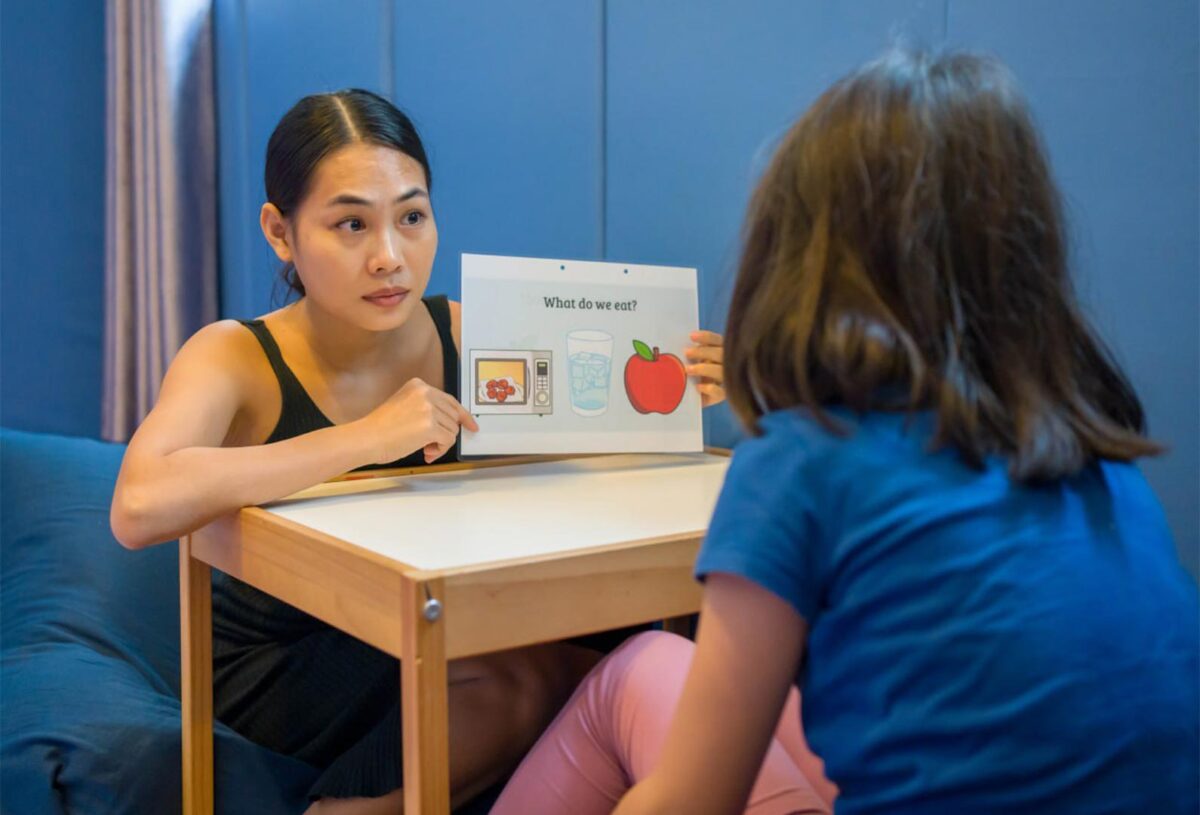
Autism is characterized by diverse neurological differences that affect communication, behavior, and social interaction. When discussing adulthood, one must recognize that the manifestations of autism often evolve. For many, challenges such as anxiety, sensory sensitivity, and difficulty with change may intensify during the transition to adulthood. Identifying these obstacles is the first step toward developing tailored strategies that address the specific needs of each individual.
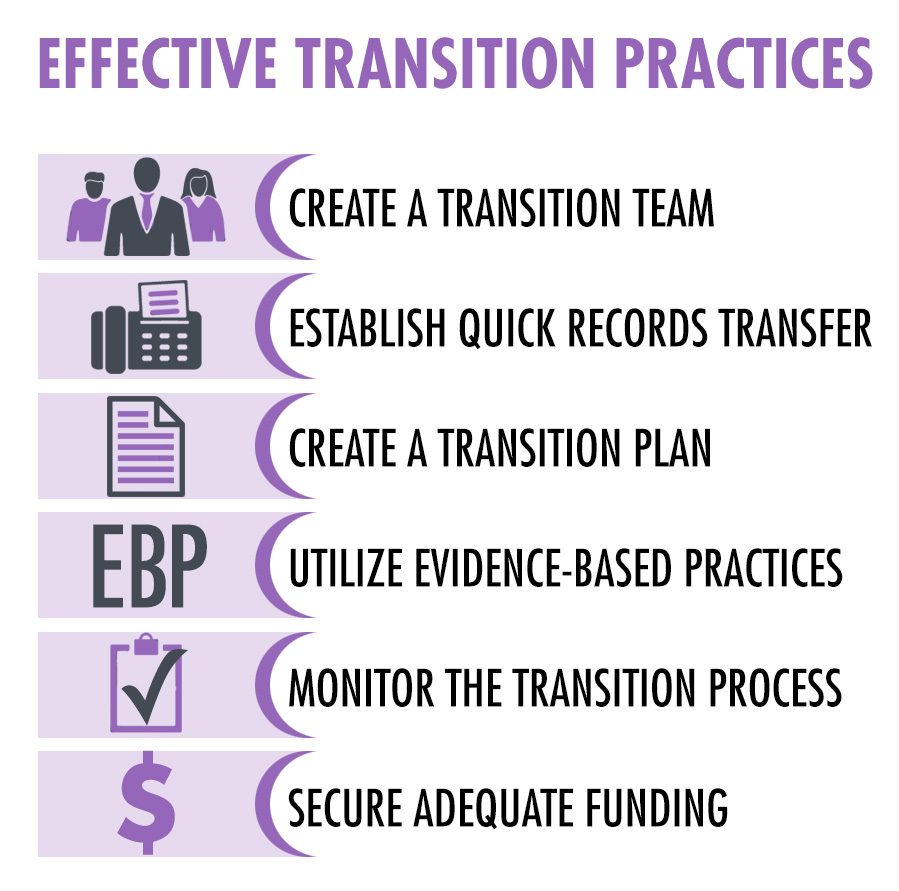
2. Education and Skill Development
The transition period is an opportune time for individuals on the autism spectrum to acquire essential life skills. Educational institutions play a crucial role in providing resources and support for students with ASD. Access to specialized programs focusing on vocational training, social skills development, and independent living is vital. These programs must emphasize practical, real-world applications, fostering skills that will be beneficial beyond the classroom.
Additionally, encouraging participation in extracurricular activities can significantly enhance interpersonal skills and boost self-esteem. Whether it’s engaging in art, sports, or community service, these experiences cultivate a sense of belonging and purpose.
3. Employment Opportunities and Career Guidance
A successful transition into adulthood often hinges on meaningful employment. The exploration of various career pathways should begin early, allowing individuals to identify their strengths and passions. Job coaching services tailored for those with ASD can assist in finding suitable roles, helping them understand workplace dynamics, and mastering interview techniques. Furthermore, companies that support neurodiversity are increasingly emerging, offering inclusive work environments that embrace different cognitive profiles.
Employers must also recognize the unique strengths of individuals with autism, such as attention to detail, dedication, and innovative problem-solving skills. By fostering an accommodating atmosphere and providing necessary adjustments, workplaces can leverage the potential of their neurodiverse employees.
4. Social Skills and Relationship Development
Social interactions can pose significant challenges for individuals with autism. Therefore, integrating social skills training during the transition period is vital. Programs that focus on peer interaction, communication prowess, and conflict resolution empower individuals to build and maintain positive relationships. Creating opportunities for structured social experiences, such as group activities or mentorship programs, facilitates connection and community building.
In addition, fostering familial support and open dialogue about relationships is paramount. Families can play an instrumental role in guiding their loved ones through the intricacies of friendships, dating, and professional relationships, helping them navigate the emotional landscape with confidence.
5. Independent Living Skills
Mastering independent living is a critical milestone during the transition to adulthood. Individuals should learn fundamental skills, including financial literacy, personal hygiene, meal preparation, and time management. Engaging in daily living activities not only promotes autonomy but also enhances self-sufficiency. Programs focused on life skills training can provide practical experiences, encouraging practice in a safe environment.
Moreover, it is vital to educate families on how to gradually encourage independence in their loved ones. Practicing patience and providing opportunities for decision-making allow individuals to cultivate confidence in their abilities.
6. Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
Addressing mental health is of paramount importance as individuals transition into adulthood. Many people on the spectrum experience heightened anxiety, depression, or feelings of isolation. Regular mental health support, whether through therapy, counseling, or support groups, can mitigate these challenges. These sessions should focus on emotional regulation practices, coping mechanisms, and problem-solving skills to foster well-being.
Creating a robust support system comprising family, friends, and professional networks can significantly enhance emotional resilience. Engaging in community initiatives, art therapy, or recreational activities that promote mental wellness can offer therapeutic benefits while also providing a sense of belonging.
7. Advocacy and Self-Advocacy Skills
Empowering individuals with autism to become advocates for themselves is crucial during this transition. Teaching self-advocacy skills enables them to articulate their needs, set personal goals, and navigate various systems effectively. This involves understanding their rights and accessing available resources. Encouraging participation in advocacy groups can further solidify their voice, allowing them to influence policy changes and promote awareness in the larger community.
Moreover, fostering resilience and a sense of agency empowers individuals to confront challenges head-on and pursue their aspirations with unwavering determination.
8. The Role of Community and Support Networks
Community involvement is vital in supporting individuals with autism during their transition to adulthood. Establishing connections with support networks, local organizations, and social services can pave the way for valuable resources and opportunities. Participation in workshops, seminars, or events can enhance skills while simultaneously fostering connections with peers facing similar challenges.
Community outreach programs tailored specifically for individuals with ASD can create safe spaces for engagement and growth. Providing accessible resources and building supportive environments strengthens the communal fabric that nurtures these transitions.
In conclusion, the transition to adulthood for individuals with autism is a multifaceted journey laden with challenges and opportunities. Comprehensive support, focused education, advocacy, and community engagement are crucial elements that contribute to successful transitions. By embracing a holistic approach, we can minimize barriers and enhance the quality of life for those embarking on this significant phase of their lives. Each individual’s path to adulthood is unique, and recognizing this diversity will ensure a future that is not only inclusive but also filled with promise and potential.