Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by a diverse range of symptoms and challenges. Individuals with autism may exhibit difficulties in communication, social interactions, and behavioral patterns that deviate from societal norms. Understanding the nuances of autism is pivotal not only for those affected but also for caregivers, educators, and communities. In exploring treatment approaches and support options, we uncover a landscape rich with possibilities for fostering growth, independence, and well-being.
At the crux of autism treatment lies the recognition of its spectrum nature. Each person with autism possesses a unique combination of strengths and challenges, necessitating a tailored approach to care. This is where an interdisciplinary methodology becomes invaluable. The fusion of pediatricians, psychologists, speech therapists, occupational therapists, and educators creates a comprehensive support system that significantly enhances outcomes.
One of the most commonly utilized treatment modalities is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA). ABA is a well-structured approach based on the principles of behaviorism, emphasizing the role of reinforcement in learning. Practitioners employ various techniques to shape positive behaviors while minimizing maladaptive ones. ABA interventions can be described as both systematic and adaptable, allowing for specific strategies that cater to the individual’s unique behavioral patterns. By applying these behavioral principles, practitioners can facilitate essential skills such as communication and social engagement, instilling a sense of confidence and competence in individuals with autism.
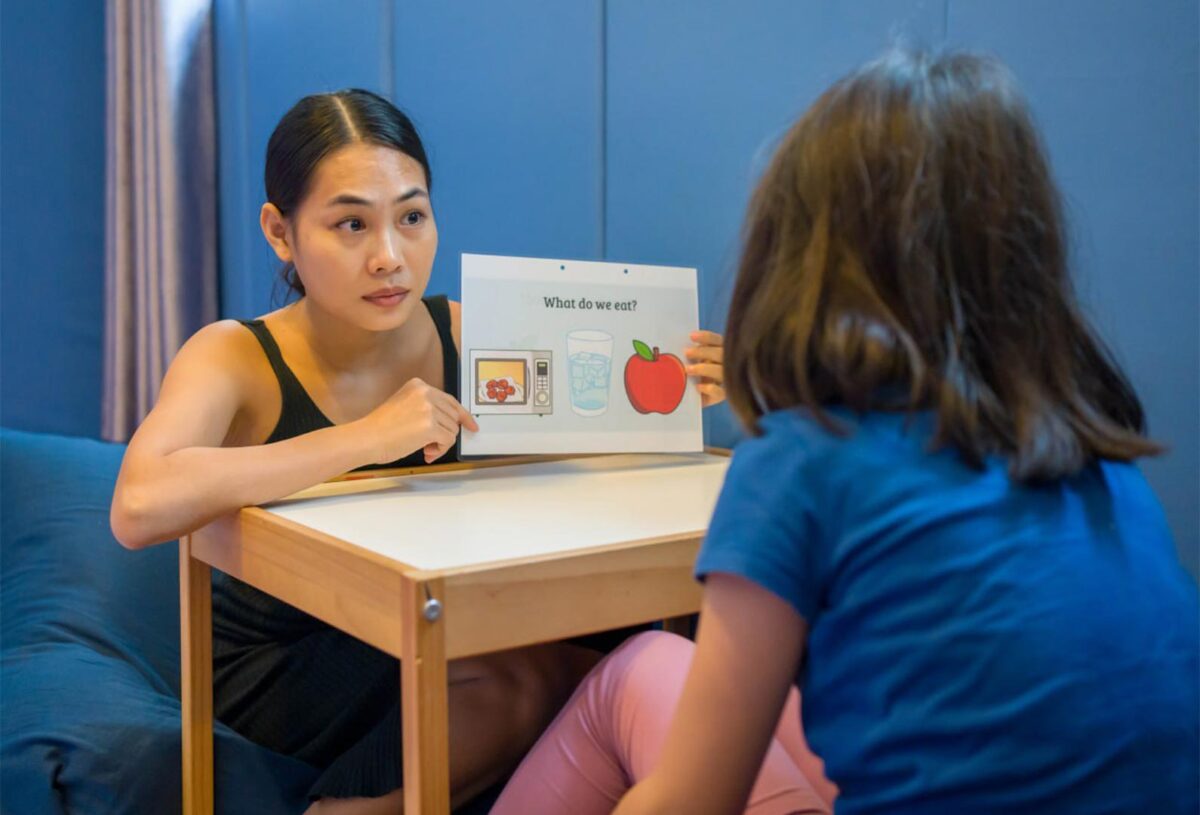
Beyond ABA, it’s essential to highlight the increasing prevalence of developmental therapies. Speech and language therapy, for instance, is integral for many individuals on the spectrum. Effective communication can significantly bolster the quality of life, leading to improved social interactions and academic performance. Speech therapists work diligently to bridge communication gaps by employing a range of strategies tailored to individual needs, whether that’s through augmentative communication devices or traditional dialogue practice. Such interventions not only enhance verbal skills but also bolster nonverbal communication, empowering individuals to express themselves more naturally.
Another pivotal component of autism support is occupational therapy (OT). This form of therapy focuses on helping individuals develop the necessary skills for daily living and achieving greater autonomy. Occupational therapists emphasize sensory integration, helping clients process sensory information in a more functional manner. Strategies such as creating calm environments, introducing sensory breaks, and developing fine motor skills contribute to improved participation in everyday activities. Consequently, individuals learn to navigate their environment more effectively, fostering independence and self-worth.
Social skills training is yet another invaluable asset in the therapeutic arsenal. This approach emphasizes the importance of social interactions and relationships, crucial areas where many individuals with autism face challenges. Through structured social skills groups or one-on-one coaching, participants engage in practical scenarios that enhance their understanding of social cues, such as body language and tone. By practicing these skills in safe environments, individuals gain confidence and build positive peer relationships, thus cultivating an essential support network.
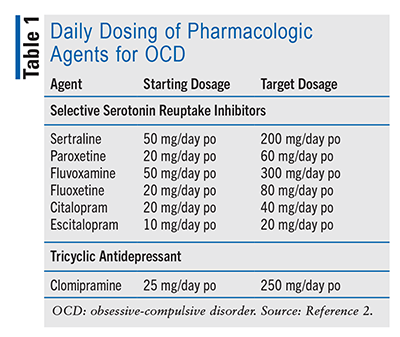
In addition to these therapeutic approaches, the role of medication in managing autism-related symptoms should not be overlooked. While no medication can cure autism, specific medications can help alleviate associated issues such as anxiety, depression, or attention deficits. The judicious use of pharmacotherapy can create a more favorable environment for behavioral interventions to take root, allowing individuals to engage more effectively with their therapies and daily life.
A collaborative approach also extends to educational support, as schools play a crucial role in a child’s development. Many educational systems are now incorporating Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) designed specifically to meet the unique needs of students with autism. These programs detail personalized goals and accommodations, ensuring that students receive appropriate support tailored to their academic and social needs. Educators are trained to implement strategies that facilitate learning and engagement, promoting inclusivity within educational environments.
In navigating the landscape of autism support, families are pivotal players. Parental involvement is essential, and support groups can offer invaluable peer connection and resources. By sharing experiences and strategies, parents can cultivate a sense of community while also empowering themselves to advocate effectively for their children’s needs. The importance of community support cannot be understated. Through organizations and local initiatives, families can access resources, therapy options, and informed guidance. This closes the gap between professional intervention and familial support, creating a holistic framework for growth.
While challenges certainly exist, there remains an abundance of opportunity for positive outcomes. Advocacy efforts are gaining momentum, increasing awareness regarding the needs of individuals with autism. These movements drive essential policy changes that promote access to therapies, resources, and educational accommodations. As society embraces a more inclusive perspective, the shift in perception surrounding autism is palpable, fostering environments where individuals can thrive.
In summary, the treatment of autism spectrum disorder encompasses a multi-faceted approach, with various therapeutic modalities working in concert to support individuals and their families. From behavioral therapies to educational accommodations, the potential for meaningful engagement and independence is profound. By embracing openness and a willingness to explore innovative support mechanisms, we stand to unlock the potential of every individual with autism, thus paving the way for a brighter future filled with possibilities.