Autism, a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by varying degrees of challenges in communication, social interaction, and behavioral patterns, has beckoned scientists and researchers throughout the decades. The multifaceted nature of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has compelled the scientific community to relentlessly investigate its etiology, symptoms, and potential therapies. Recent studies have unveiled groundbreaking insights, transforming our understanding of autism, and elucidating its intricate web of influences. This article delves into some of the most profound breakthroughs and emerging findings, highlighting the fascination surrounding this enigmatic condition.
The landscape of autism research has shifted remarkably over the past few years. Traditionally viewed through a narrowly defined lens of deficits, contemporary studies have begun to illuminate the peculiar strengths that many individuals with autism possess. This paradigm shift underscores the notion that autism is not merely a collection of limitations but a unique cognitive profile that encompasses both challenges and remarkable capabilities. Numerous case studies and neurocognitive assessments reveal that individuals on the spectrum often exhibit heightened perceptual sensitivity and exceptional skills in areas such as mathematics, music, and visual arts.
What drives this fascination is the sheer diversity within the autism spectrum itself. From those who are non-verbal to highly articulate individuals successfully navigating various professional environments, autism manifests in myriad forms. One particularly intriguing study examined the role of genetics in this diversity, offering tantalizing clues about the biological underpinnings of ASD. Researchers have identified numerous genetic variants associated with autism, leading to the hypothesis that these genetic anomalies might interact with environmental factors, contributing to the wide variance in symptoms and abilities observed in individuals.
Another captivating area of inquiry revolves around the concept of a “mismatch” hypothesis. This theory suggests that the neurodevelopmental trajectories of individuals with autism may diverge significantly from neurotypical norms, resulting in distinctive cognitive processing styles. For instance, a study utilizing advanced neuroimaging techniques revealed that certain brain networks in individuals with autism might operate differently, particularly those involved in social cognition and sensory processing. Such insights elucidate why some individuals on the spectrum may struggle with conventional social cues while simultaneously excelling in areas that require focused attention and intense concentration.
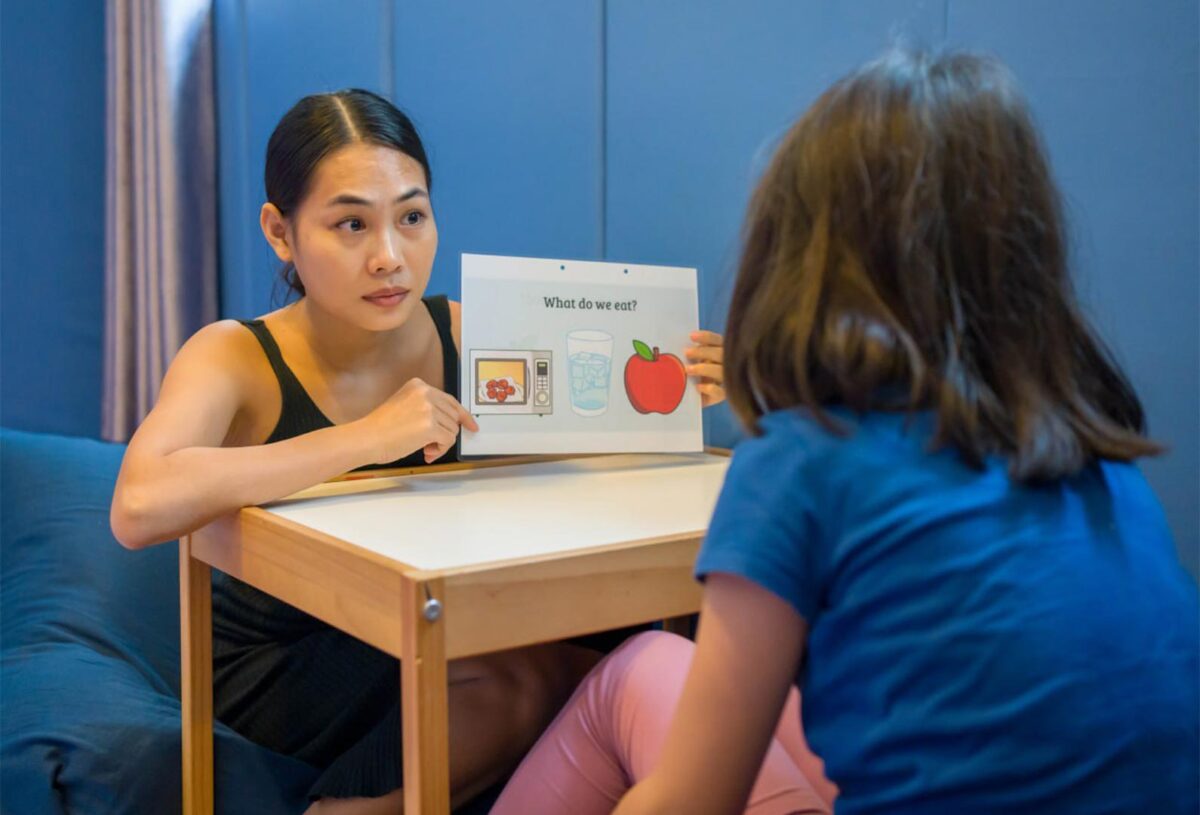
As research progresses, the importance of early diagnosis and intervention has emerged as a crucial finding. Neurological studies indicate that early brain development plays a pivotal role in shaping a child’s social and communicative abilities. Interventions targeting developmental milestones—initiated as early as 18 months—have shown promising results. Techniques like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and early intensive behavioral intervention (EIBI) are now being fine-tuned based on advancements in understanding autism’s neuroplasticity, underscoring the necessity of personalized approaches tailored to each individual’s profile.
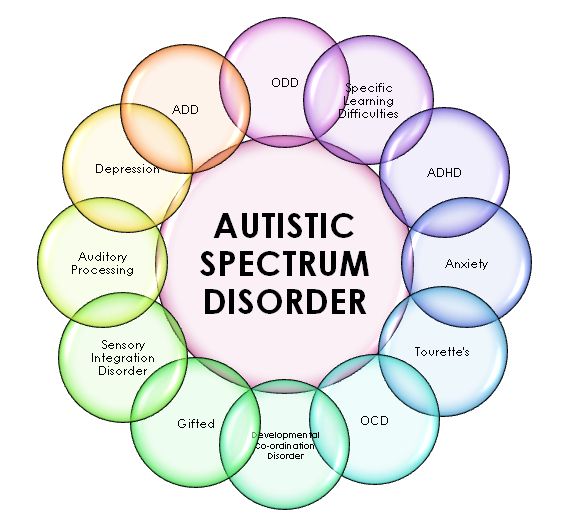
Moreover, the relationship between autism and co-occurring conditions has garnered increased attention. Research has consistently shown a notable prevalence of co-morbid disorders—such as anxiety, depression, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)—among individuals diagnosed with autism. Emerging findings suggest that these co-occurring conditions can exacerbate challenges experienced by individuals on the spectrum, highlighting the imperative to adopt a holistic treatment strategy that addresses the full spectrum of an individual’s health and well-being.
The advent of technology has ushered in innovative methodologies for studying and supporting individuals with autism. Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a novel therapeutic tool, enabling individuals to traverse simulated environments that mimic real-life social interactions. Such immersive experiences can serve as practice grounds for developing social skills, offering intriguing insights into the neural mechanisms involved in social cognition. Furthermore, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in analyzing large datasets continues to yield new hypotheses and potential interventions, paving the way for more refined and individualized treatment options.
Perhaps the most profound area of exploration lies in understanding the lived experiences of individuals with autism and their families. Research indicating the significance of neurodiversity posits that embracing the unique attributes of individuals on the spectrum can foster a more inclusive society. Personal narratives and qualitative studies are revealing how acceptance, understanding, and appropriate support can empower individuals with autism, allowing them to thrive rather than merely survive in neurotypical environments. This advocacy for inclusion resonates deeply, challenging societal norms and encouraging a shift toward a more accepting worldview.
As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities surrounding autism, one undeniable truth emerges: each discovery opens new avenues of inquiry while simultaneously posing further questions. The intertwining of genetic, biological, and environmental factors underscores the necessity for ongoing research, emphasizing the need for interdisciplinary collaboration between geneticists, psychologists, and sociologists. Such collaborations can foster a richer understanding of autism, ultimately informing more effective policies and practices that respect and support individuals on the spectrum.
In conclusion, the journey into the realm of autism, characterized by persistent inquiry and burgeoning insights, is far from complete. Breakthrough studies and emerging findings continue to deepen our comprehension, revealing the unique abilities of individuals with autism while simultaneously addressing the myriad challenges they face. As we foster a more nuanced understanding of autism, we inch closer to a society that not only recognizes the profound complexities of the spectrum but embraces the vibrant diversity it represents. The ongoing quest for knowledge promises not only to illuminate the scientific underpinnings of autism but also to enrich the human experience by championing empathy, understanding, and inclusion.