Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) encompasses a vast range of neurodevelopmental differences that profoundly alter the way individuals communicate, interact, and perceive the world. The multifaceted nature of autism requires an equally complex approach to research, which continues to evolve dramatically. This article will delve into the current trends in autism research, exploring promising breakthroughs, controversial methodologies, and the evolving perspectives that influence our understanding of this intricate condition.
Understanding the Neurobiology of Autism
One of the most exciting trends in autism research is the increasing focus on the neurobiological underpinnings of the disorder. Researchers have made significant strides in identifying specific genetic mutations and brain structure variations associated with ASD. The use of advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), allows scientists to visualize brain activity and connectivity patterns in individuals with autism. These insights promise to revolutionize our understanding of how autism manifests in the brain, potentially guiding more tailored interventions.
Furthermore, investigations into the gut-brain axis have gained traction. Studies suggest a correlation between gastrointestinal dysfunction and the severity of autism symptoms. This emerging field posits that microbial imbalances in the gut may influence neurodevelopmental trajectories, thus prompting fresh approaches to treatment, including dietary modifications and probiotics. Such insights are tantalizing, opening new avenues that bridge physical health with cognitive and emotional well-being.
Behavioral Interventions: Evolving Strategies
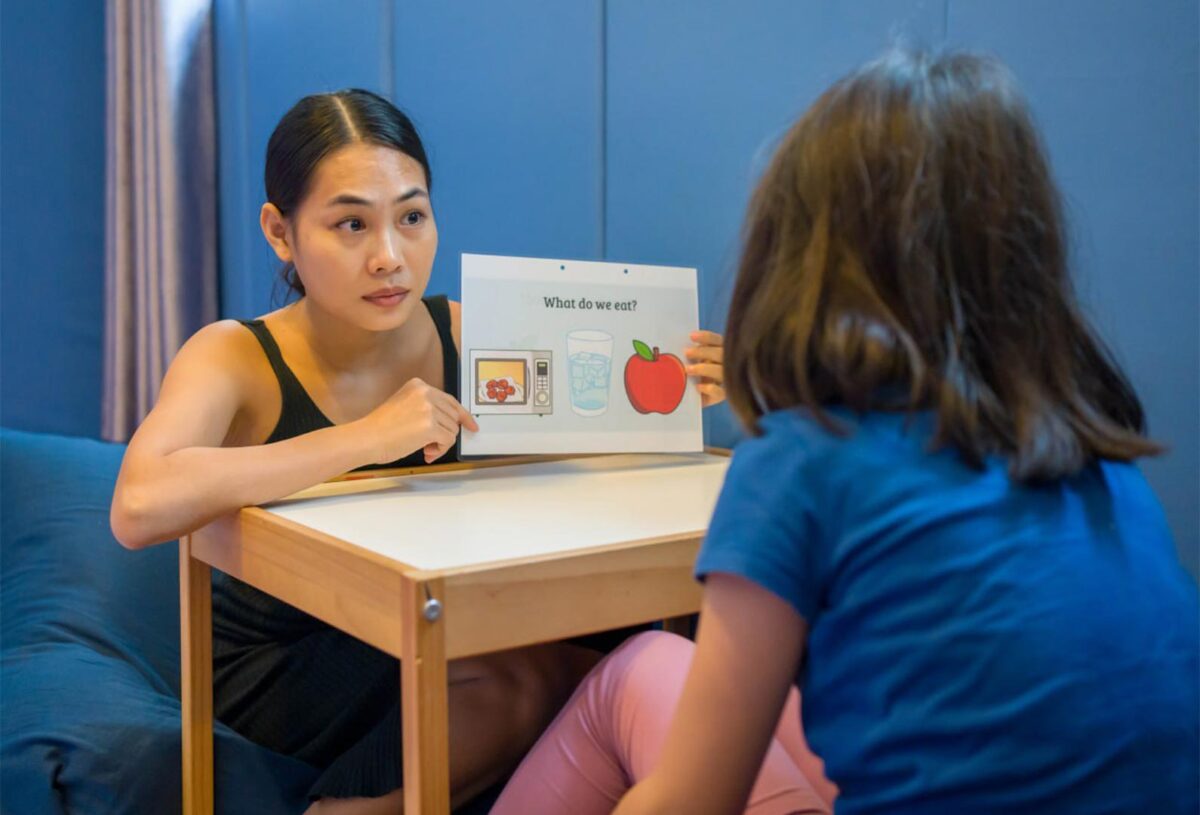
Traditional behavioral interventions, particularly Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), have long been the cornerstone of autism therapies. However, recent trends indicate a shift towards more holistic and individualized approaches. Researchers are increasingly advocating for interventions that focus on enhancing quality of life, promoting independence, and fostering social connections rather than merely minimizing undesirable behaviors. This paradigm shift emphasizes the necessity for person-centered planning, where the individual’s preferences, strengths, and unique challenges dictate the direction of the intervention.
The incorporation of technology in behavioral interventions represents another groundbreaking trend. Digital platforms and mobile applications provide innovative means for delivering social skills training and enhancing communication. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are making waves as tools for simulating real-life scenarios in a controlled environment, allowing individuals with autism to practice social interactions without the apprehension of actual social settings.
Sensory Processing and Autism: A New Frontier
For many individuals on the autism spectrum, sensory sensitivities are pervasive and challenging. Contemporary research is increasingly focusing on sensory processing as a crucial aspect of autism. Experts are investigating the neurological mechanisms that underlie atypical sensory experiences, aiming to develop strategies and treatments that can help mitigate distress and enhance daily functioning.
Innovative sensory integration therapies are being designed to support individuals in navigating their sensory environments with greater ease. This shift towards recognizing sensory processing as an integral component of autism reaffirms the need for varied and adaptable approaches to support, acknowledging the unique ways in which individuals experience the world around them.
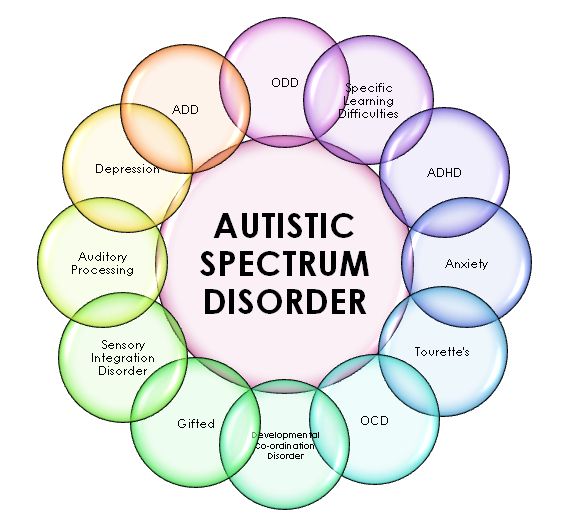
Autism and Comorbidities: The Broader Picture
Autism seldom exists in isolation; the presence of comorbid conditions such as anxiety, depression, ADHD, and epilepsy is prevalent. Current research is emphasizing the importance of recognizing and addressing these co-occurring conditions. Understanding the interplay between ASD and these comorbidities is vital for developing comprehensive treatment plans that consider the full spectrum of an individual’s experiences.
Interdisciplinary approaches are gaining momentum, with collaborations between psychologists, psychiatrists, occupational therapists, and educators becoming increasingly common. This interconnected methodology ensures that treatment encompasses the myriad aspects of an individual’s health, paving the way for more effective and inclusive strategies.
Advocacy and Inclusion: A Shift in Perspective
As research progresses, so too does the shift in societal attitudes toward autism. The neurodiversity movement has gained traction, promoting the understanding that autism is not merely a deficit to be fixed but rather a different way of being that offers unique strengths and perspectives. This evolving perspective has led to increased advocacy efforts surrounding rights, inclusion, and acceptance for individuals on the spectrum.
An emphasis on self-advocacy is emerging, with individuals with autism taking an active role in shaping policies and practices that affect their lives. The focus on empowerment and agency represents a transformational shift in the narrative around autism, encouraging society to appreciate the diverse contributions that individuals with autism can offer.
Future Directions: Ethical Considerations and Responsible Research
As the field of autism research advances, ethical considerations become increasingly prominent. The dialogue surrounding genetic testing, for instance, raises questions about the implications of utilizing such information. The potential for misinterpretation of genetic predisposition and the subsequent societal stigmatization necessitates careful ethical scrutiny.
Similarly, the commercialization of autism therapies and interventions requires vigilance to prevent exploitation. Researchers and practitioners must strive to uphold the dignity and welfare of individuals on the spectrum, ensuring that evidence-based practices guide their approaches rather than market trends.
In conclusion, the landscape of autism research is evolving with remarkable dynamism. By emphasizing neurobiological insights, embracing holistic interventions, acknowledging sensory experiences, addressing comorbidities, fostering advocacy, and maintaining ethical rigor, the field is poised for transformative advancements. Each trend not only promises to unlock greater understanding but also stands to redefine the narratives that surround autism, igniting curiosity and acceptance in equal measure.